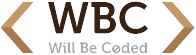E-mail use has increased over time. Companies and people alike are using it as a marketing tool. They send sensitive marketing information, financial reports and newsletters among other things via e-mail. The question of whether the intended recipient received the message is a non-issue. This is because most e-mail providers will tell you if you have sent the e-mail to a non-existent recipient or not. To know whether the person the e-mail was intended for has opened it or not is another issue altogether.

Knowing this is the only way that one can gauge the effectiveness of the e-mail. Luckily, Google Analytics have the answer to this problem. There is a way that one can know if the recipient of your e-mail opened the mail in question, when and where they did that or if they just spammed it.
GOOGLE ANALYTICS E-MAIL TRACKING
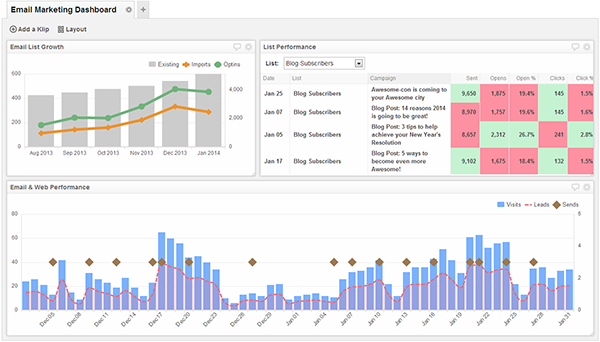
Email service provider tracking can be used to check if a client opened one’s email or not. It however has more limited capabilities compared to Google Analytics. The latter boasts of being able to give tracking information in real time. It can also give demographic information complete with a specific location. What is even better is that one can do the tracking themselves without professional tech help. The service is also free. All one has to do is embed an image tag into the html of the e-mail in question. The unique web address (URL) of the embedded image contains all the information needed for Google Analytics to do its job.
This information is the sent email campaign, the recipient’s account information and the sender’s account. This means that for one to use Google analytics as an e-mail tracking device, they need an account complete with a tracking ID from Google Analytics (GA). This means that if one has a g-mail account, all one needs to do is integrate the GA system into the account. If one does not have an account, one can go straight into creating a GA tracking ID on their site. After one has successfully embedded the image in the e-mails and sent them out, it is important to specify how he or she wants to receive the reports.
URL BREAKDOWN
A sample of the embedded URL as explained above is http://goo.gl/jpOjDP We look at what each segment of the link signifies from the last typed all the way up.
|
URL Component |
Explanation |
| cn=Campaign Name | Campaign Name identifies the campaign to you |
| cm=email | Campaign Medium could segment social vs. email, etc. |
| cs=newsletter | Campaign Source allows segmentation of campaign types |
| el=recipient_id | Event Label specifies a unique identification for this recipient |
| ea=open | The Event Action helps specify exactly what happened |
| ec=email | Campaign Medium could segment social vs. email, etc. |
| t=event | Tells Google Analytics this is an Event Hit Type |
| cid=CLIENT_ID_NUMBER | A systematic tracking ID for the customer |
| tid=UA-12345678-1 | Your Google Analytics Tracking ID |
| v=1 | Protocol version within Google Analytics |
HOW TO USE THE RESULTS
These reports generated by Google Analytics are useful as they give insights into customer behavior such as at what time most e-mails are opened. This is useful information as it tells a company about the most visited parts of their site, the time when most people visit the website, their physical locations among other things. This can help in future market planning and forecasts.
It can also help in determining what time the website can be brought down for restructuring as one can accurately average when it has the least traffic. Over time, one can learn each individual customer’s interests by the mails they open and those they do not. The reports from the tracking can help better strategize and come up with better marketing plans. At the end of the day, even if one is not in business, it helps to know if one’s intended e-mail recipient opened their e-mail or not. It at least makes judging them easier.
OUR FINAL ADVICE
Knowing the efficiency of your e-mail campaigns is very important as such tools could generate up to 40% additional revenue of existing customers if you deal with a high retention based businesses. Additionally, it is a tool that could be used to reveal the most active clients, as well as a guidance towards tailoring messages towards certain people.
Thin content is also known as low-quality content. Low quality contents are textual materials of any website that are not useful for a user, but rather made to manipulate rating in search engines.
According to Google thin content is:
- 1. Pages with content that is not unique.
- Texts that are not unique are texts that were already added to / indxed by Google before Google bot visits your web-page. In order to avoid this – one needs to rewrite at least 50% of the text or delete the text.
- 2. Duplicates of already existing pages
- A great number of duplicate pages create additional load for Google bot during indexation and such duplicate pages are also linked within your site and drain link juice from your site as a whole – that negatively affects site’s rating.
For example, online shops often face a problem where a certain category generates hundreds of URLs through filters and all of them are indexed in search..
Example: domain.com/tires/?page=2&site=32&price=20 etc.
- 3. Pages that contain too little content
- For example: online shops with thousands of goods that do not contain characteristics.
- 4. Websites with pages that do not generate any traffic for a long time (especially from the search)
- For example, online shops that do not delete hundreds of thousands of old goods pages or a video archive of a TV-channel, that includes thousands of materials that are 20 years old and that are not of a high demand by searchers.
- 5. “Tasteless or Useless” content that does not attract traffic
- Very often owners of websites follow the recommendations regarding the creation of new content and rewrite (reuse) the same topic for a million times. For example, some publications that contain only general phrases rather than examples, instructions and so on.
- 6. Texts, overloaded with key words
- It is not recommended to overload any text with key words in order to receive top results. The approximate percentage of key words per all words – should vary between 2.0 – 2.5%.
Of course, if there are only several of such pages that are overloaded with keywords, you won’t get a penalty, but if its’ percentage is over 50% you are risking to get penalized and as a result – to lose up to 95% of search traffic.
How to detect thin content on a website?
- Comment from Matt: https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/2604719?hl=en
1. Pages with texts that are not unique
You have to check all content for plagiarism (authenticity) by one of the tools:
https://www.google.com.ua/search?q=Plagiarism%20Checker
Acceptable levels of similarity are below 50% (across webpage or website).
What to do with the content that is not unique?
-You should rewrite it or delete from the website.
2. Duplicates of existing pages
To check the website for duplicate pages you can use Web Site Auditor – that software will show you the duplicating tags that are often the duplicate pages.
You can also look up the duplicate meta tags through Google Webmaster Tools (HTML Improvements).
What to do with duplicates?
One option is to 301 permanent redirect it; bind through “rel=canonical” tags or simply by removing those pages = “404” (not recommended).
3. Pages that contain too little content
This information can be gathered manually or with a help of a programmer, he will show the pages that have little to no text at all.
4. Websites that have pages that did not bring any traffic for a long time (especially from the search)
This information can be gathered with the help of Google Analytics. You should go to Behavior → All website pages. You need to download all the pages for the past year and also generate the list of all the pages from website. Then you need to sort only the pages without traffic from the search.
5. Useless content that does not attract traffic
Just like in the previous paragraph you can use Google Analytics. However, it is worth mentioning that the pages could have had traffic at the moment of their publication, yet lose it over time. So if the content is not useful then it is worth deleting.
6. Texts, overloaded with key words
If the texts are useful and quality, but overloaded with keywords you should reduce the keywords density and after re-indexation by Google – SERP’s will improve and web traffic will flow.
How to detect poor content?
- 1. Use Google Webmasters that show duplicating tags.
- 2. Google Analytics – will help to detect the content that does not attract traffic.
- 3. Detecting pages that contain little contact can be done manually or by programming a script.
- 4. Detecting duplicates of tags can be done with the help of any “full website audit” tool (for example Web Site Auditor by Link Assistant).
- 5. Auditing density of keywords – http://tools.seobook.com/general/keyword-density/
(Must be less than 3%).
How long will it take to remove the penalties for thin content?
It depends on the size of the website and the date when the algorithm will refresh its data. Usually, Google re-indexes small websites within a month, large ones – every three to six months.
The algorithm refreshes its data every “one-two” months.
Conclusion
It is wise to check you website for thin content and perform the above mentioned actions in order to avoid problems with the website in the future.
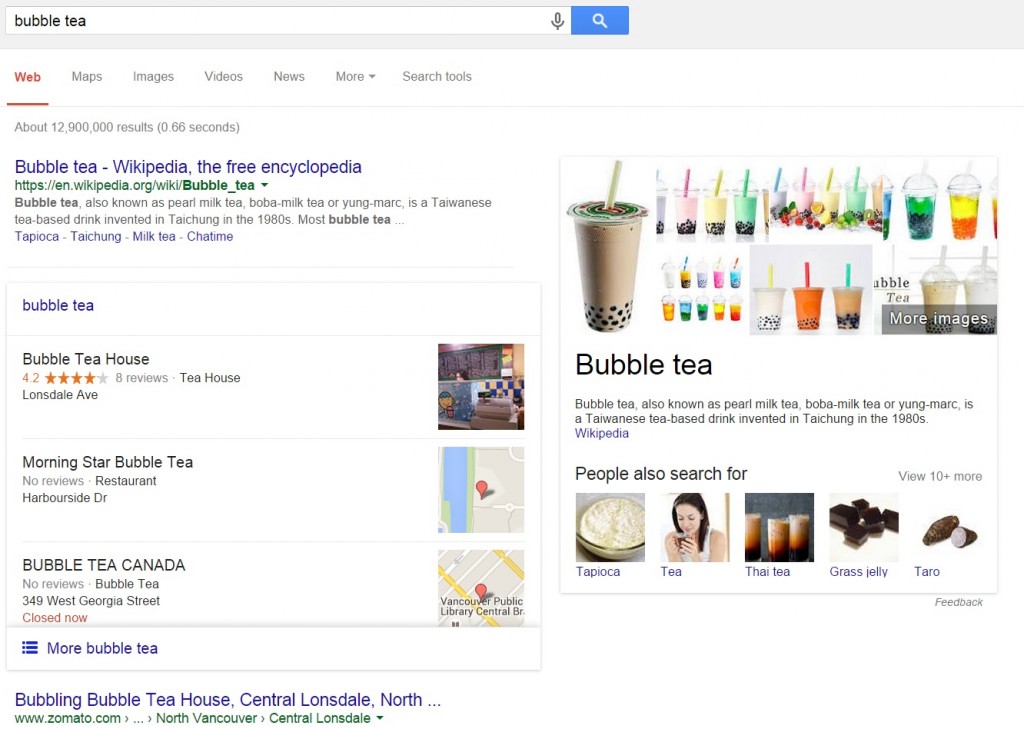
The majority of websites have a brand search traffic, a traffic that is generated by the brand name of the company /website or by the name of its products. Usually this name is unique and it can generate close to 40% of all traffic if you have a high customer retention / return rate.
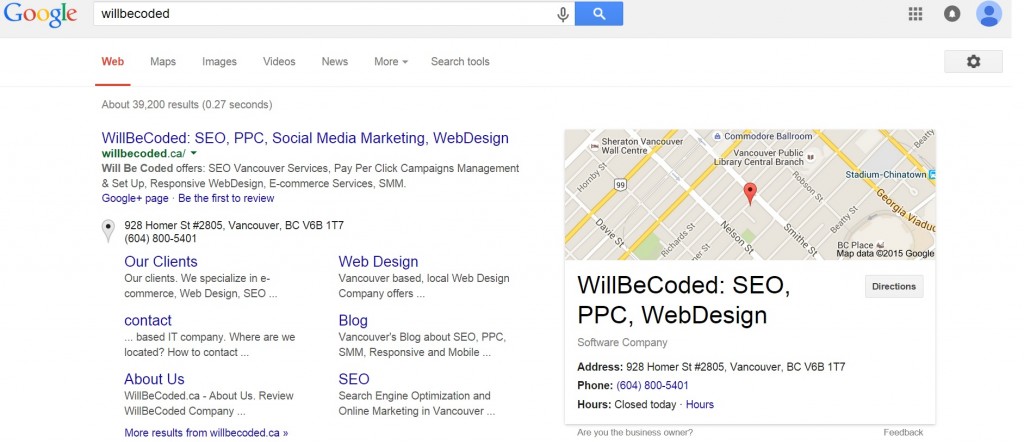
Google gives an opportunity to get not only advanced search snippet for your website by brand keywords (usually it consists of only additional references), but also additional pieces of information from your G+ account for local business. That includes: logo, geographical location, address, phone numbers, type of business, business hours and also feedbacks about your company.
In order to receive these search results you need to go to www.google.com/local/manage/ webpage and add your company. It is very important to fill in 90% of information about the company and add obligatory elements like logo, address, type of business, phone number and business hours.
Besides, if you are a local company – filled out G+ account will help your website to appear in the map search results as well as on the map. For this to be done, it is important for you to add company-related keywords to the company name field and short description of your company. One of the advantages of this method is that it is much easier to rank higher than your competitors even by being in the map results. For this you only need to do the following:
- 1. Register at local listings of your region www.google.com/local/manage/.
- 2. Fill in all fields in the G+ account (for local business account).
- 3. Get real feedback from real users of your region (for local business account).
- 4. Implement Rel=Publisher Tag (Google says that this tag will help you to get better positions on the maps).
- 5. Add your website to your business information by following https://support.google.com/business/answer/3039617
How to implement Rel=Publisher Tag
On your website’s main page insection of HTML code add the following tag: <link href=”https://plus.google.com/example” rel=”publisher” /> that points to your google plus page.
Rich snippet will be showed for brand name only. Mixed domain keywords will not trigger the rich snippet.